"There is nothing called state. There are events and the story we tell about what it means."
Flux allows you to quickly build an application in CQRS way without the hassle of a messaging system like RabbitMQ or Kafka inbetween your command and read model services.
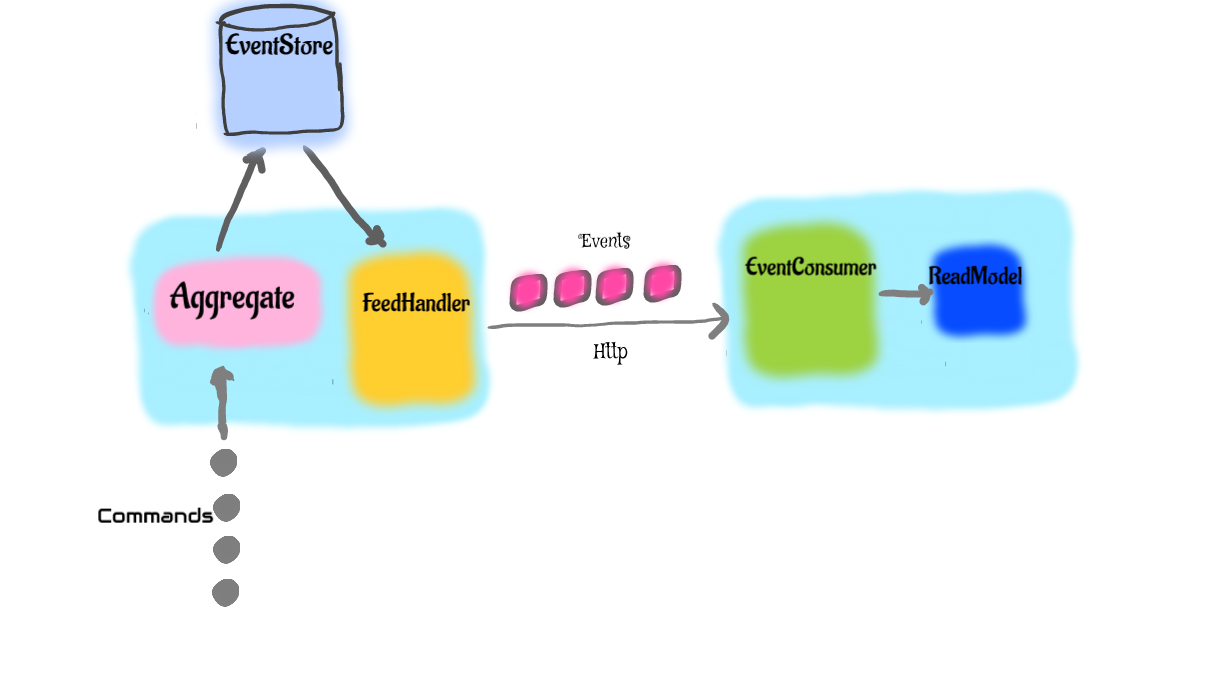
It's a good practice to have one command service per Aggregate (as per DDD terminology) and various read model/view services. the command service stores the events that are emited by each command and expose the same as a json feed for the consumers (read model services) to consume in regular intervals allowing you to easily decouple commands and "read model" services.
Aggregates accepts commands and generates events.
This is how you can define an aggregate in Flux:
import(
"github.com/yehohanan7/flux"
"github.com/yehohanan7/flux/cqrs"
)
//Account is an aggregate
type Account struct {
cqrs.Aggregate
Id string
Balance int
}
//Initialize the aggregate
acc := new(Account)
acc.Aggregate = cqrs.NewAggregate("account-id", acc, flux.NewBoltStore("path/to/database"))The last argument is an EventStore, which provides an implementation to store and retrieve events - there are 2 implementations at the moment an inmemory one and a boltdb implementation
store := flux.NewMemoryStore()Once you have the aggregate initialized, you can execute commands on it which will in turn emit events, make sure to update the state of the aggregate through a handler method (prefixed with the name Handle) on the aggregate
//My event
type AccountCredited struct {
Amount int
}
//Command
func (acc *Account) Credit(amount int) {
acc.Update(AccountCredited{amount})
}
//Event handler to allow you to update the state of the aggregate as a result of a command
func (acc *Account) HandleAccountCredited(event AccountCredited) {
acc.Balance = acc.Balance + event.Amount
}
//Execute command
acc.Credit(100)
acc.Credit(150)
if err := acc.Save(); err == cqrs.Conflict {
//this error is due to concurrent modification of the aggregate, you should retry the request
}Feed handler allows you to publish the events as a json feed for the outside world.
router.HandleFunc("/events", flux.FeedHandler(store))
router.HandleFunc("/events/{id}", flux.FeedHandler(store))Same feed exposed by the endpoint /events is as below
{
"description": "event feed",
"events": [
{
"event_id": "47d074c3-ba83-40e2-8720-804b73a202b9",
"url": "http://localhost:3000/events/47d074c3-ba83-40e2-8720-804b73a202b9",
"aggregate_name": "*account.Account",
"aggregate_version": 0,
"event_type": "account.AccountCreated",
"created": "Fri Apr 7 15:19:18 2017"
},
{
"event_id": "174a40b6-104a-4be5-a352-4e61b524d3dc",
"url": "http://localhost:3000/events/174a40b6-104a-4be5-a352-4e61b524d3dc",
"aggregate_name": "*account.Account",
"aggregate_version": 1,
"event_type": "account.AccountCredited",
"created": "Fri Apr 7 15:19:27 2017"
}
]
}Event consumer allows you to consumer the events emitted by the aggreate in another service. you can start the event consumer like shown below, in the below example the consumer polls the aggregate service every 5 seconds to check for new events.
//stores the offset to know where to consumer from after a restart
offsetStore := flux.NewMemoryOffsetStore()
consumer := flux.NewEventConsumer("http://entityservicehost:port/events", 5 * time.Second, []interface{}{AccountCredited{}}, offsetStore)
eventCh := make(chan interface{})
//Start consuming
go consumer.Start(eventCh)
//Fetch the events and build your read models
for {
event := <-eventCh
switch event.(type) {
case AccountCredited:
fmt.Println(event.(AccountCredited))
}
}You could pause,resume & stop the consumer
consumer.Pause()
consumer.Resume()
consumer.Stop()Read model is nothing but the result of how you interpret the events provided by the consumer shown above.
There is a simple example application here if you would like to refer
mongodb as your event & offset store using mgo
import (
"gopkg.in/mgo.v2"
"github.com/yehohanan7/flux"
"github.com/yehohanan7/flux/mongodb"
)
// Create mongodb session
session, err := mgo.Dial("localhost")
// ...
// Create event store
eventStore := flux.NewMongoStore(&mongodb.MongoEventStoreOptions{
Session: session,
Database: "example", // optional
EventCollection: "event",
AggregateCollection: "aggregate",
TransactionCollection: "transaction",
})
// Create offset store
offsetStore := flux.NewMongoOffsetStore(&mongodb.MongoOffsetStoreOptions{
Session: session,
Database: "example", // optional
Collection: "offset",
StoreId: "a_unique_id_for_consumer",
})- Optimize consumers by using websockets/server push
- Support postgres
- publish metrics to graphite
- Support option to emit events to external systems if required.